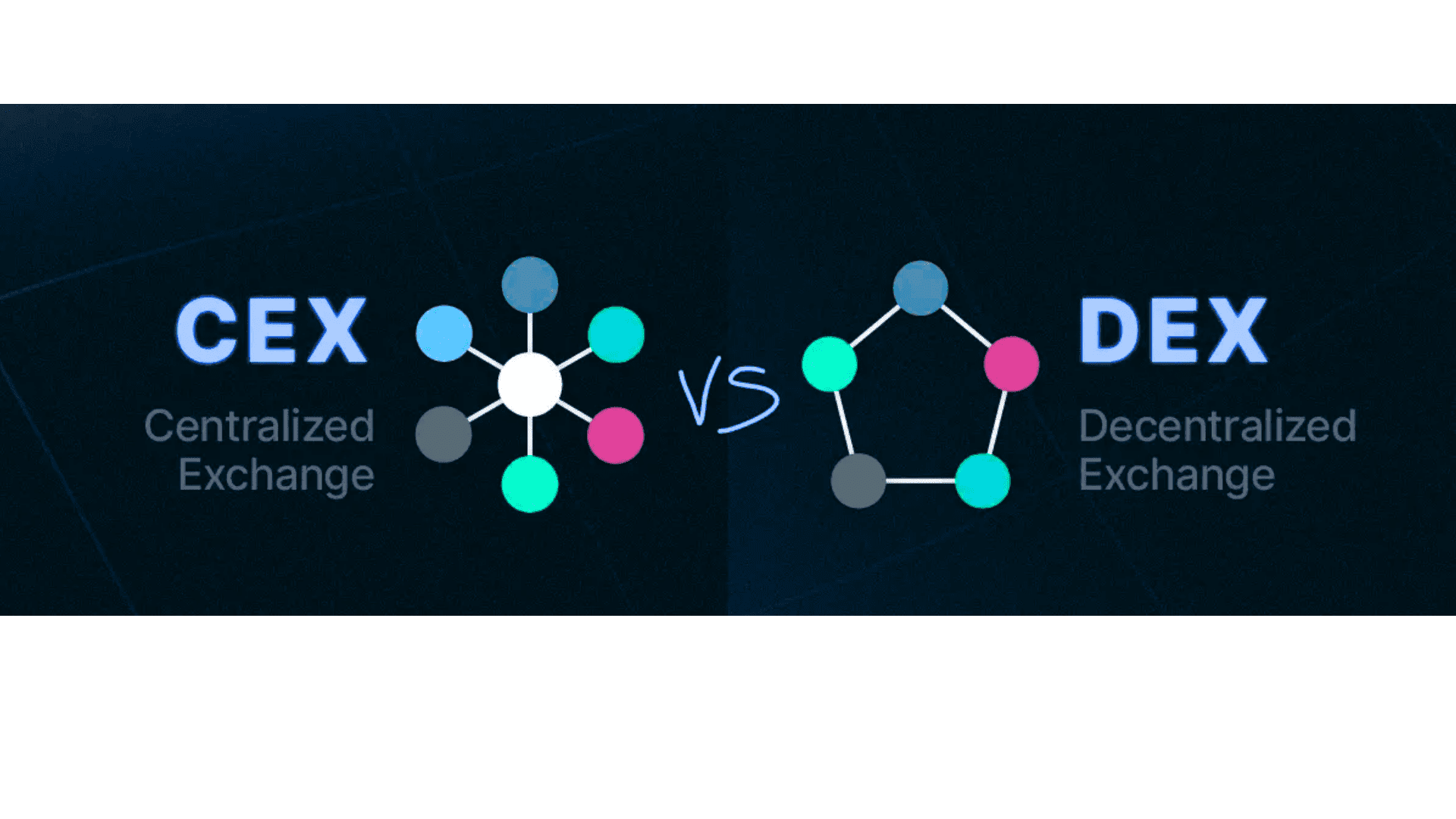
Difference Between CEX and DEX
In the world of cryptocurrency trading, two major types of exchanges dominate: Centralized Exchanges (CEX) and Decentralized Exchanges (DEX). While both serve the same primary function — facilitating cryptocurrency trading — they do so in very different ways.
Let’s break down the key differences between these exchanges to help you understand which one suits your needs better.

1. What is a Centralized Exchange (CEX)?
A Centralized Exchange (CEX) is a platform controlled by a central authority or company. These exchanges act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, managing the order book, custody of funds, and transaction execution.
Key Features of CEX:
Centralized control: A single entity manages the platform.
User funds stored: The exchange holds the funds in its own wallets.
Higher liquidity: Centralized control means more liquidity and faster trades.
User-friendly interface: Easier for beginners.
Regulation: Often operates under the regulations of a specific country.
Examples of CEX:
Binance
Coinbase
Kraken
KuCoin
- Gate.io
- Crypto.com
What is a Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?
A Decentralized Exchange (DEX), on the other hand, is a platform that allows users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other, without the need for a central authority. The exchange uses smart contracts and blockchain technology to facilitate trades in a peer-to-peer manner.
Key Features of DEX:
Decentralized control: No central authority; users trade directly with one another.
User-controlled funds: Traders retain control of their private keys and funds.
Lower liquidity: Liquidity depends on the number of active users and the pool of assets available.
Higher security: Less susceptible to hacking since there’s no central point of failure.
Privacy: Typically does not require KYC (Know Your Customer) or identity verification.
Examples of DEX:
Uniswap
SushiSwap
PancakeSwap
1inch
Key Differences Between CEX and DEX
| Feature | Centralized Exchange (CEX) | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Controlled by a single entity | Controlled by a decentralized network |
| Liquidity | High liquidity due to centralized control | Lower liquidity, depending on user participation |
| Security | Vulnerable to hacking attacks | More secure due to no single point of failure |
| Fees | Typically higher fees for transactions and withdrawals | Usually lower fees due to decentralized nature |
| Regulation | Often regulated by government authorities | Less regulated, operates globally |
| User Experience | Easier to use, more intuitive | Can be complex and less user-friendly |
| Privacy | Requires KYC (Know Your Customer) verification | No KYC required, users retain privacy |
| Examples | Binance, Coinbase, Kraken | Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap |
Pros and Cons of CEX vs. DEX
Centralized Exchanges (CEX)
Pros:
Higher liquidity makes for faster and larger trades.
Easy-to-use interface, ideal for beginners.
Regulated: Offers some degree of consumer protection.
Cons:
Vulnerable to hacking since the exchange holds users’ funds.
Centralized control: A single point of failure.
Requires KYC which compromises privacy.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX)
Pros:
Privacy: No KYC is required.
Control over funds: You retain control of your private keys.
More secure: Less vulnerable to hacking because there is no central entity.
Cons:
Lower liquidity, which might result in slippage.
Higher complexity: May not be as user-friendly for beginners.
Longer transaction times due to reliance on the blockchain.
Which is Better?
The choice between CEX and DEX depends on your goals and preferences.
Use a CEX if you want higher liquidity, ease of use, and don’t mind sharing your personal information (KYC).
Use a DEX if you value privacy, security, and control over your funds, even if it means lower liquidity and more complex trading.